The 1979 Referendums
The results in ScotlandThe results in Wales
The introduction of devolution legislation in 1976 was largely the product of nationalist pressures on the Government. James Callaghan's Labour government had a majority of only three after the 1974 (October) election and by 1977 had no majority at all after a series of by-election defeats. The government was therefore vulnerable to pressures from the Scottish National Party and Plaid Cymru, who between them won 14 seats at the election (SNP 11, Plaid Cymru 3). The Kilbrandon commission had reported in 1974, recommending the establishment of a Scottish parliament and endorsing the principle of devolution.
A combined Scotland and Wales Bill was introduced in November 1976. It gained a second reading only after referendums in both Scotland and Wales had been conceded. The Shadow Secretary of State for Scotland, Alick Buchanan-Smith, and one of his front benchers, Malcolm Rifkind, resigned their posts when the Shadow Cabinet decided to oppose its second reading. On the first day of committee 350 amendments were put down. Michael Foot, (then Lord President and Cabinet Minister responsible for the devolution bill) was reluctant to impose a guillotine. After nearly 100 hours of debate only three and a half clauses of the bill had been considered. A guillotine motion was tabled but defeated in February 1977. The Bill was withdrawn.
In November 1977 separate Bills for Scotland and Wales were introduced, with support from the Liberals. This reduced opposition from those who had previously opposed the combined Bill on the grounds that the Welsh did not really want devolution. This time the guillotine motion was won.
As the committee stage was nearing its end, it scrutinised an amendment from Labour backbencher George Cunningham. It required the Secretary of State to lay before Parliament an order repealing the Act unless at least 40% of the eligible electorate voted "yes". The amendment was strongly opposed by the Government, but they lost the vote by 166 votes to 151.
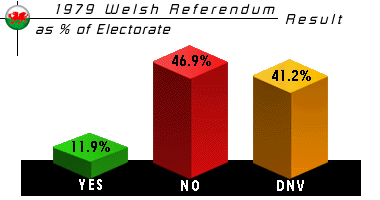
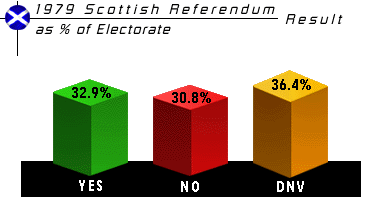
In the referendum, on 1 March 1979, Scotland voted in favour of devolution by 52% to 48% - but only 32.9% of the electorate had joined the majority. In Wales the vote was against devolution, by 80% to 20%. The Acts were repealed the next month.
The Government was not helped by the extent of internal dissent within the Labour party. There was an active Labour 'Vote No' campaign in Scotland, of which Brian Wilson was Chairman, and Robin Cook a Vice-Chairman together with Tam Dalyell.
In Wales, Neil Kinnock was among those who campaigned for a "no" vote. During the last few days of the campaign in Wales, the pro-devolution Labour party -TUC group argued that a "No" vote would be a vote for the Tories, and a vote against the Government. This was a gamble that did not pay off; the scale of the "No" victory meant that those who had campaigned against the government could feel vindicated.
A motion of no confidence in the government was tabled by the Conservatives and supported by the SNP, the Liberals and eight Ulster Unionists. This motion was carried by one vote on 28 March 1979. The next day Callaghan announced that Parliament would be dissolved.
Question: Do you want the provisions of the Scotland Act 1978 to be put into effect ?
The 1979 Results:
Scotland:
| Yes | 1,230,937 | (51.6%) | ||
| No | 1,153, 502 | (48.4%) | ||
| Rejected ballot papers | 3,133 | |||
| Electorate | 3, 747,112 | |||
| Turnout | 63.6% |
Wales:
Question: Do you want the provisions of the Wales Act 1978 to be put into effect?
| Yes | 243,048 | (20.3%) | ||
| No | 956,330 | (79.7%) | ||
| Rejected ballot papers | 3,309 | |||
| Electorate | 2,038,049 | |||
| Turnout | 58.8% |